Capturing and utilizing carbon dioxide (CO2) is essential to achieving a clean energy, net-zero carbon future. And reimagining the alignment of industry and infrastructure presents exciting opportunities for states and regions across the country. Deploying CO2 transport and storage infrastructure will enable key sectors of our economy to dramatically reduce their carbon emissions while sustaining and growing domestic industry, manufacturing, and energy production and the high-wage American jobs they support.
Analysis conducted for the State Carbon Capture Work Group through its Regional Carbon Capture Deployment Initiative (RDI) shows the potential for capturing CO2 from industrial and power generation facilities that share common infrastructure to lower costs and achieve economies of scale for CO2 transport, use, and geologic storage.
Carbon capture deployment at industrial facilities and power plants and buildout of associated CO2 transport infrastructure in 21 states across the Midwest, Great Plains, Gulf Coast, and Rockies regions can support an annual average of up to 68,000 project jobs and 35,800 ongoing operational jobs over a 15-year period, while capturing and managing 592 million metric tons of CO2 per year.
The RDI’s national analytical team conducted a review of major emitting facilities to identify near-term opportunities for capture retrofit among the nation’s industrial and power facilities. Each facility’s eligibility for the Section 45Q tax credit, unique operation patterns, and announced retirement date were all considered in this process. Facilities were analyzed at the unit level in order to identify capturable streams of CO2 within each facility and right-size capture equipment to those specific levels.
The maps depicted below aim to help inform a broader emerging discussion of industrial decarbonization and the particular needs of carbon-intensive industries such as steel, cement, refining, and basic chemicals. These sectors’ industrial processes often have limited or no abatement options beyond carbon capture, utilization, and storage. At the same time, they provide high-wage jobs and revenues and often form the backbone of local and regional economies.
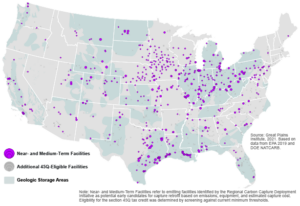
Over 500 facilities identified nationwide as potential near-term candidates for capture retrofit, symbolized here with pink dots, are collectively responsible for nearly 1 billion metric tons of emissions annually. Additional facilities that would be expected to qualify for the Section 45Q tax credit by meeting minimum capture thresholds, depicted here with light gray dots, emit an additional 1.1 billion metric tons of CO2 per year.
NEAR-TERM CARBON CAPTURE OPPORTUNITIES ACROSS THE US
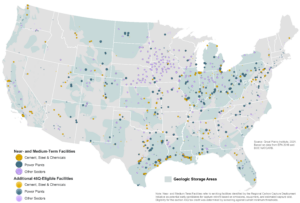
Cement, steel, refining, and basic chemicals facilities comprise over 30 percent of all facilities identified as near-term capture opportunities. Carbon capture, utilization and storage can help decarbonize these difficult-to-abate sectors, while bolstering local economies and protecting and creating high-wage jobs.
CARBON CAPTURE OPPORTUNITIES IN KEY INDUSTRIAL SECTORS
Learn more about this analysis on our Carbon Capture Ready website: carboncaptureready.betterenergy.org
This blog was originally published by Great Plains Institute.
